Options of the 2D-COS Control Window: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Type of 2D spectrum''': defines the type of the 2D-COS analysis. Valid options are:<br> | '''Type of 2D spectrum''': defines the type of the 2D-COS analysis. Valid options are:<br> | ||
* Pearson scaling - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pearson, or unit variance scaling. Pearson scaling is also used in statistical total correlation spectroscopy [STOCSY] and statistical heterospectroscopy [SHY]) | *Pearson scaling - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pearson, or unit variance scaling. Pearson scaling is also used in statistical total correlation spectroscopy [STOCSY] and statistical heterospectroscopy [SHY]) | ||
* Pareto scale 0.75 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.75 | *Pareto scale 0.75 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.75 | ||
* Pareto scale 0.50 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.50 (Pareto scaling in the strict sense) | *Pareto scale 0.50 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.50 (Pareto scaling in the strict sense) | ||
* Pareto scale 0.25 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.25 | *Pareto scale 0.25 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.25 | ||
* stat synchronous - the classical synchronous 2D (covariance) spectrum | *stat synchronous - the classical synchronous 2D (covariance) spectrum | ||
* stat asynchronous - the classical asynchronous 2D spectrum | *stat asynchronous - the classical asynchronous 2D spectrum | ||
* disrelation - allows to calculate the absolute of the 2D disrelation spectrum | *disrelation - allows to calculate the absolute of the 2D disrelation spectrum | ||
* fft synchronous - alternative implementation to obtain the synchronous 2D correlation spectrum by means of the fast Fourier-transformation approach | *fft synchronous - alternative implementation to obtain the synchronous 2D correlation spectrum by means of the fast Fourier-transformation approach | ||
* fft asynchronous - alternative implementation to obtain the asynchronous 2D correlation spectrum by means of the fast Fourier-transformation approach | *fft asynchronous - alternative implementation to obtain the asynchronous 2D correlation spectrum by means of the fast Fourier-transformation approach | ||
'''Spectral regions for 2D-COS analysis''': allows to define the [x,y] spectral ranges for 2D-COS analysis | '''Spectral regions for 2D-COS analysis''': allows to define the [x,y] spectral ranges for 2D-COS analysis | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 9 April 2025
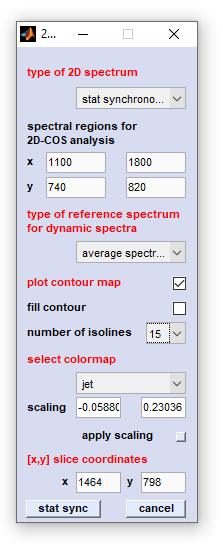
Type of 2D spectrum: defines the type of the 2D-COS analysis. Valid options are:
*Pearson scaling - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pearson, or unit variance scaling. Pearson scaling is also used in statistical total correlation spectroscopy [STOCSY] and statistical heterospectroscopy [SHY]) *Pareto scale 0.75 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.75 *Pareto scale 0.50 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.50 (Pareto scaling in the strict sense) *Pareto scale 0.25 - the synchronous 2D spectrum with Pareto scaling. The parameter α equals 0.25 *stat synchronous - the classical synchronous 2D (covariance) spectrum *stat asynchronous - the classical asynchronous 2D spectrum *disrelation - allows to calculate the absolute of the 2D disrelation spectrum *fft synchronous - alternative implementation to obtain the synchronous 2D correlation spectrum by means of the fast Fourier-transformation approach *fft asynchronous - alternative implementation to obtain the asynchronous 2D correlation spectrum by means of the fast Fourier-transformation approach
Spectral regions for 2D-COS analysis: allows to define the [x,y] spectral ranges for 2D-COS analysis
Type of reference spectrum: defines the type of reference spectrum to obtain the dynamic spectrum. Valid options are no reference (spectrum), average spectrum (default), first spectrum and last spectrum.
Plot contour map: plots a contour map instead of an interpolated surface map where the color is proportional to the 2D-COS functional values.
Fill contour: creates a filled contour map
Number of isolines: defines the number of isolines in contour / filled contour maps
Select colormap: the type of color maps used to plot surface maps, or to plot the isolines in contour maps
Scaling: permits to modify manually the color map by entering the minimal and maximal z-values into the appropriate edit boxes
Apply scaling: color map scaling values are immediately applied to the 2D correlation spectrum
[x,y] slice coordinates: settings required to plot 1D correlation slices, or to create [x,y] feature plots